Belt pulley mechanisms are systems which utilize the generated rotational motion to drive another mechanism, change its rotational power or speed, and are used by almost every business.
Advantages:
- It has the capability to operate at a wide speed range.
- The belts do not require lubrication.
- They are cheaper than chains for low power and low rotation rate.
- Flat belts are the best mechanism for very high speed transmissions.
- They slide under the loads that are too heavy to move, therefore they serve as a protective equipment against mechanical damage in shafts.
- They are a suitable solution for long axle offsets.
- Because no lubrication is required, they can operate in the open.
Disadvantages:
- Except for the timing belt, they are not used for exact timing tasks, as shifting can occur.
- Belts are easily affected by chemicals and heat.
- If there is a problem, they can cause vibrations, operate loudly, and create noise.
Things to Watch Out For While Installing the Belt-Pulley Systems:
- In V-belts, the belt is not allowed to sink more than 1mm into pulley groove compared to first assembly.
- Under normal operating conditions, the belt must not exceed 60 ° C.
- No corrosive matters, grease or oil mist should be present in the working area (contact area).
- Relaxation checks must be performed on the belts.
- Pulleys must be subjected to balancing process after production.
- Care must be taken to avoid impacts on pulleys during assembly.
- The belts should never be forced with equipments such as levers or screwdrivers.
- Basic Sizes in Belt-Pulley Systems
Flat Belts:
The torque flat brakes are able to transmit is calculated in the same way it is done with band brakes;
Interim operations can be followed from band brakes section.
Here, P1 is the tension on the tight side and P2 on the loose side, μ is the coefficient of friction, and φ is the total contact angle of the belt on the pulley. The required belt tension Pi depends on the elastic properties of the belt, and is generally calculated as follows:
If we accept that belt-pulley system is moving as slowly as required, the inertia forces of the belt can be ignored. The belts remain under the influence of centrifugal forces as they normally move quite fast during the power transmission. As a result of the centrifugal force, Pc force occurs on the belt. The resulting Pc is expressed as follows.
Here;
ml : Mass per unit length of the belt
V : Linear velocity of the belt
r :Pulley radius
The Pc force needs to be added to the equations above. Accordingly, the new equation is expressed as follows.
V-Belts:
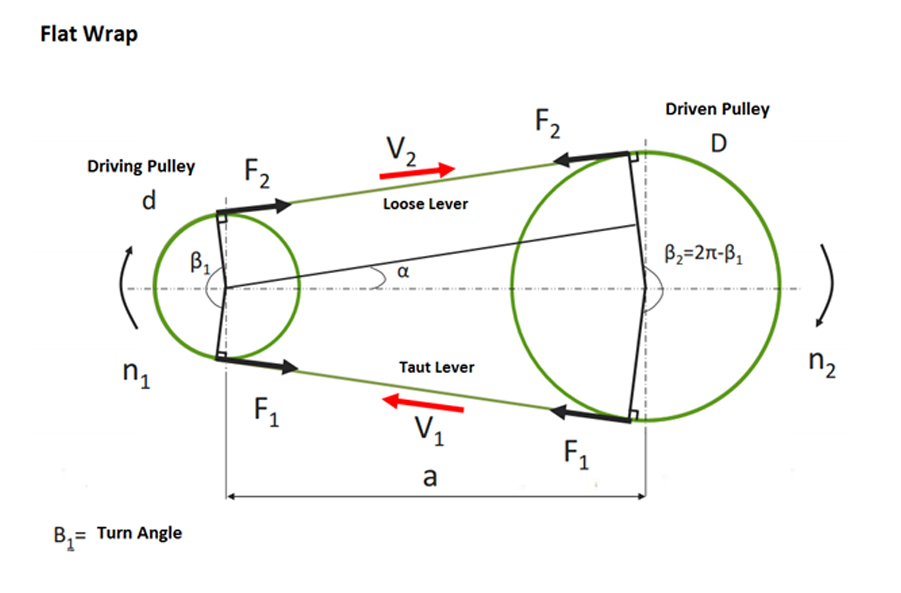
| Size | Formula | |||||
| Wrapping Angle | 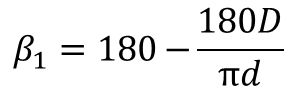 | |||||
| Belt Length | 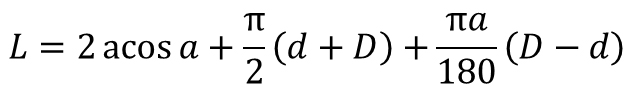 | |||||
| Belt Length (practical) | 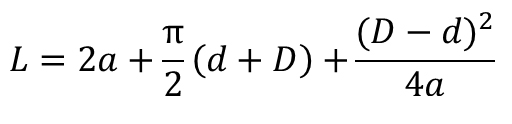 | |||||
| Pulley Diameter | 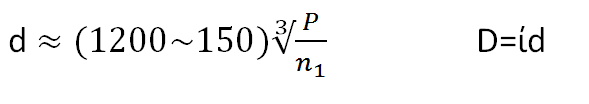 | |||||
| Belt Inclination Angle | 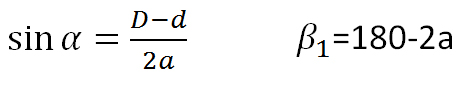 | |||||
Problem:
The electric motor drives a 19kW machine part at 1750rpm using multiple V-belts. Size is 5V-belt β = 18 ° and the unit mass of the belt is 0.215gr / mm. The pitch diameter of the motor pulley is 94 mm and the wrapping angle of the belt is 165 °.
Calculate how many V-belts are to be used, assuming that the tension load in the belt is maximum 672 N and the friction coefficient is 0.20.
Given:
Power: 19 kW, rotation speed 1750 rpm, belt type, β = 18, unit weight = 0.215 gr / mm, Pulley diameter = 94 mm,ф = 165, Pmax = 672N and ɥ = 0.20
Solution:
ve T=
r
Pc is not known here.
T=(=(672-117.5)(94/(2x1000))=26.1 Nm
T=9550=> P=
=
=4.78 kW/kayış
Number of Belts ==3.97 belts, and the number of belts is 4.
Taper Bushing Tightening Table
| Suggested Key Torque Values for Tightening Taper Bush | |
| Bushing No | Screw Tightening Torque (Nm) |
| 1008 | 5,6 |
| 1108 | 5,6 |
| 1210 | 20,0 |
| 1215 | 20,0 |
| 1310 | 20,0 |
| 1610 | 20,0 |
| 1615 | 20,0 |
| 2012 | 30,0 |
| 2517 | 50,0 |
| 2525 | 50,0 |
| 3020 | 90,0 |
| 3030 | 90,0 |
| 3525 | 115,0 |
| 3535 | 115,0 |
| 4030 | 170,0 |
| 4040 | 170,0 |
| 4535 | 190,0 |
| 4545 | 190,0 |
| 5040 | 270,0 |
| 5050 | 270,0 |







No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you for Contacting Us.